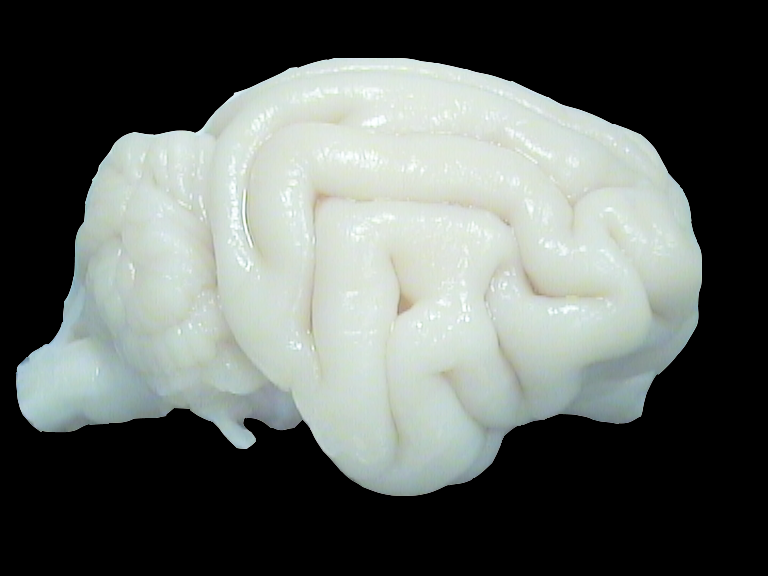
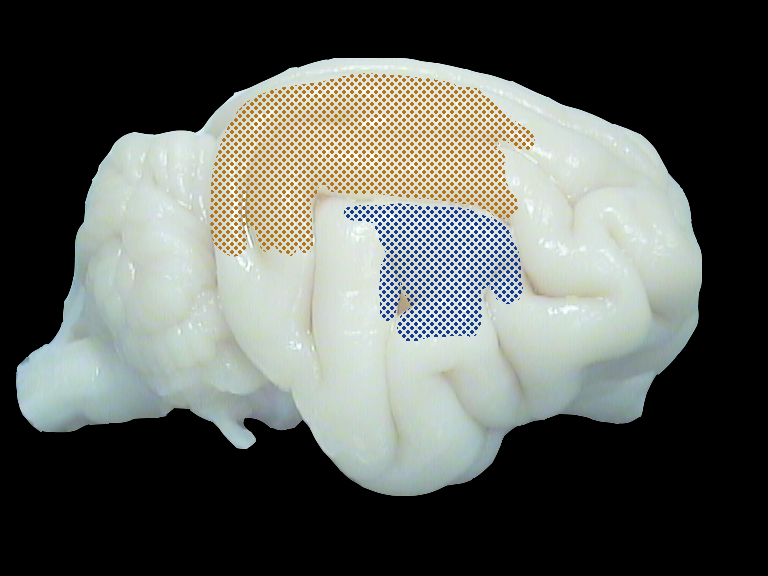
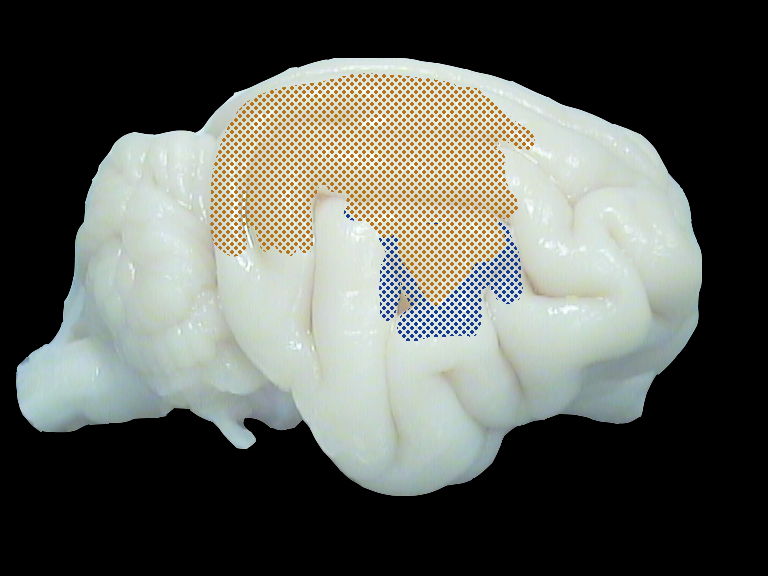
Cat brain. Shown are the direct neighbouring visual and auditory zone (DZ) along the suprasylvian sulcus. Recording in both sides of the sulcus in order to study cross-modal plasticity in the congenitally deaf brain.
The reconstruction of electrode tracks in the cat brain along the suprysylvian sulcus. Electrode tracks were reconstruced from histological slices followed by a 3D reconstruction.
Comparison of visual evoked responses in the congenitally deaf and hearing brain. Squares show the strength of activity on the visual (top) and auditory (bottom) side of the suprasylvian sulcus. In the congenitally deaf brain, visual responsiveness is increased in the auditory cortex, indicating cross-modal plasticity.